
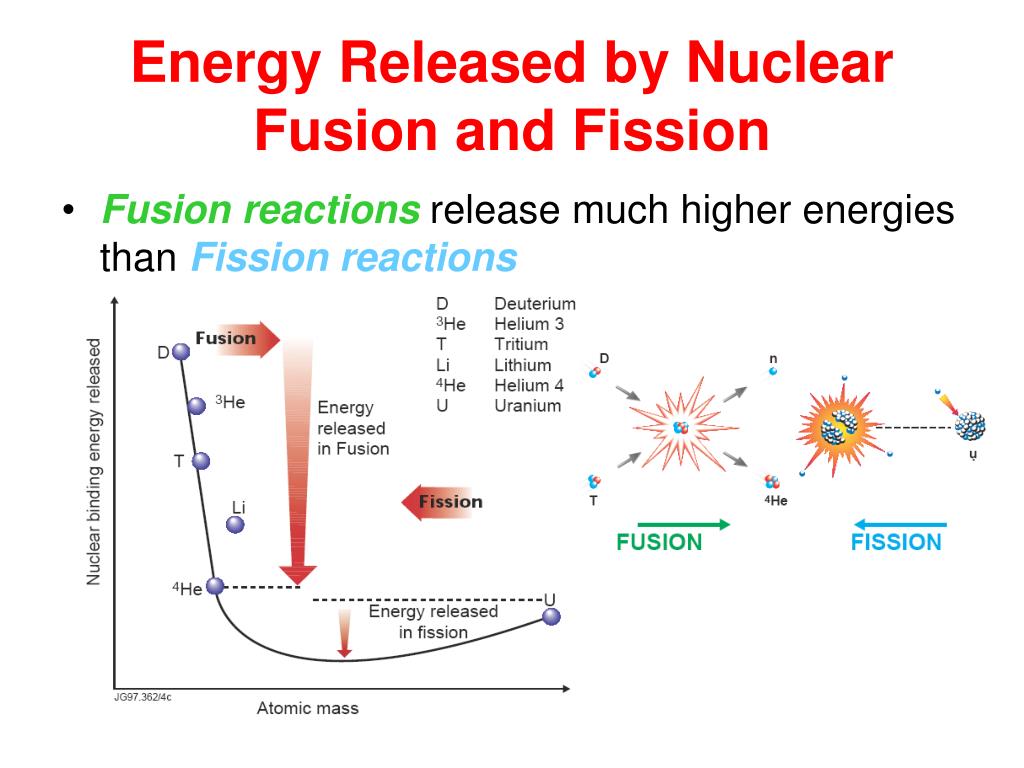
Since the water is continuously reused in this setup, the amount of water used is kept relatively low. In some nuclear power plants, the steam is then sent to a different structure called the “cooling tower,” where it’s cooled and condensed back into liquid water. This steam is then used to spin a turbine, the blades of which are attached to generators that produce electricity. The high temperatures that result from a fission reaction in the reactor core are used to heat water in the power plant, which creates steam. The process takes place in a nuclear reactor inside a nuclear power plant. In today’s world, nuclear technology relies entirely on nuclear fission, so we’ll start by describing how nuclear fission produces energy. It’s worth understanding how these mechanisms are different, as it plays a key role in their respective advantages and disadvantages. How Do Fission and Fusion Both Produce Energy?īoth fusion and fission are nuclear processes that produce an enormous amount of energy through different physical mechanisms. The fission products that result from this process then cause a chain reaction, in which the original atom is broken apart with a neutron, which releases more high-energy neutrons that disintegrate more atoms, and so on.įission reactions produce an enormous amount of energy that can in turn be used to generate electricity that powers homes and businesses. The neutron must be traveling quickly enough to overcome the atom’s binding energy, causing the protons and neutrons in the atom’s nucleus to come apart. This is achieved by firing a neutron at an atom of an element like uranium-235. Unlike nuclear fusion, which fuses nuclei, nuclear fission splits them apart. Nuclear fission is a technical term for fission reactions in which one heavier nucleus is broken down into multiple lighter nuclei. It produces more energy than most other kinds of fusion reactions (and at lower temperatures than other elements), which is why it’s of so much interest to researchers. The DT reaction creates a neutron, a helium atom, and a large amount of energy. These nuclear reactions release energy, which can be harvested to provide power wherever it is needed.Īlthough nuclear fusion can occur among many different elements, today many researchers are looking at the so-called deuterium – tritium fusion reaction, a reaction that occurs between two isotopes of hydrogen. Because smaller, lighter nuclei are fusing into a single nucleus, the process is called fusion. Nuclear fusion is a technical term for fusion reactions in which two light nuclei combine together into one heavier nucleus.

With this context established, we can turn to a discussion of nuclear fusion. They each contain one proton but different numbers of neutrons - deuterium has one neutron and tritium has two. For instance, deuterium and tritium are two isotopes of hydrogen. The number of neutrons can vary from one atom to the next, however, and these are known as isotopes. Hydrogen atoms always have one proton while helium atoms always have two, and so on. The nucleus is orbited by a cloud of electrons, which are negatively charged.įor any given atom, the number of protons determines what element it is. A nucleus is made up of positively-charged protons and neutrally-charged neutrons (meaning they have no charge). Most of the physics relevant to nuclear energy deal with changes to atomic nuclei. An atom is the basic unit of matter -anything with mass and takes up space is made up of atoms. Understanding the nuclear reactions involved in both fusion and fission is easier if you have a refresher on the structure of atoms. fusion, how these two power sources are alike, how they’re different, and how they can be used to fuel our clean-energy future. Let’s learn more about nuclear fission vs. nuclear fission - is the most viable in the foreseeable future. That said, there remain many questions about nuclear energy, including which option - n uclear fusion vs. Nuclear energy is one such alternative energy source that has been part of the United Stages energy mix for decades. The climate is changing, and as a result, many people are hard at work looking for alternative sources of power to lower the emissions of greenhouse gases like CO2.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
